Industry 4.0 and IoT: The Impactful Role of IoT
Introduction
Industry 4.0 is in the early stages of reinventing how companies design, manufacture, and distribute their products. Technologies such as IoT, cloud computing, robotics, and AI are now deeply integrated into manufacturing and related industries. Industry 4.0 transforms the way companies conceive, produce, and deliver products by creating a connected and intelligent value chain – promoting seamless collaboration among suppliers, logistics providers, manufacturers, and end customers. | Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 refers to the 4th industrial revolution, characterized by the integration of digital technologies, automation, data connectivity, and smart manufacturing processes in the industrial sector. This paradigm shift aims to create more efficient, flexible, and interconnected systems to enhance productivity and decision-making in manufacturing and related industries.
|
Background
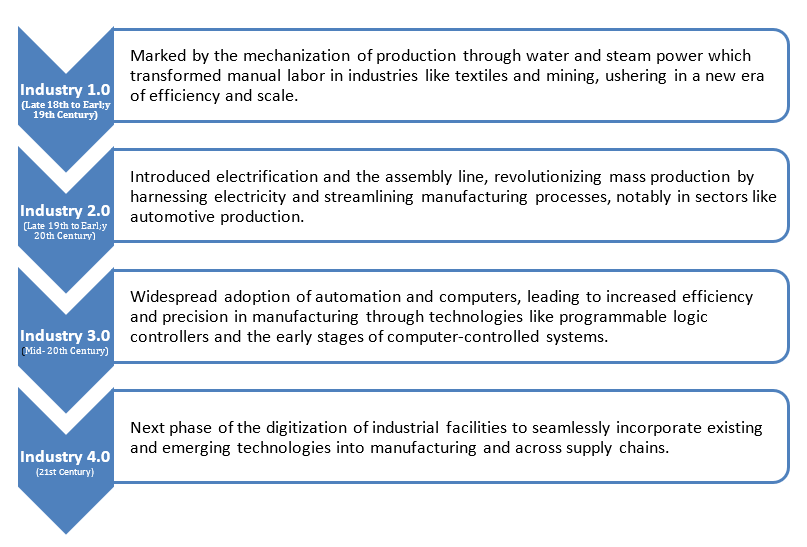
The evolution of industry has been classified into four distinct phases, each characterized by transformative technological advancements that reshaped the landscape of manufacturing and related industries.
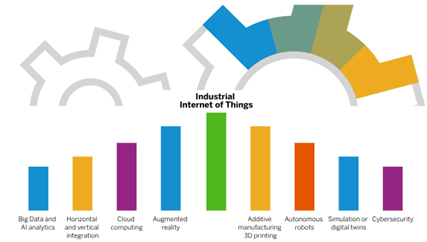
Industry 4.0 is driven by existing, but rapidly evolving technologies such as IoT, Big Data, Robotics, Augmented Reality (AR), 3D Printing, Cybersecurity, and Cloud Computing, and emerging disruptive technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Digital Twins as depicted in
At the core of the next phase of digital transformation, IoT (or Industrial IoT) stands as an essential technology, utilizing devices like sensors, actuators, RFID and Bluetooth tags, vehicle and asset trackers, wearable devices, and more. These IoT devices serve to interconnect people, products, equipment, and processes to unlock previously unavailable business insights, fostering a paradigm shift in how companies optimize their manufacturing operations and associated supply chains.
This constant flow of data enables companies to monitor and analyze industrial operations with unprecedented granularity. Through IoT platforms with Big Data (Data Analytics) capabilities, companies gain the capability to process vast amounts of information efficiently. This, in turn, empowers them to make data-driven decisions, respond rapidly to changing conditions, and enact predictive maintenance measures.
IoT’s impact extends beyond providing detailed data insights within a company as it serves as the foundation for connectivity throughout the entire value chain. By interlinking key value chain components, IoT is a key enabler to the creation of smart factories and intelligent supply chains.
Examples of Industry 4.0 improvement areas enabled by IoT include:
- Supply Chain Optimization: IoT transforms logistics management by utilizing vehicle and asset trackers for end-to-end (E2E) visibility throughout the supply chain. With streamlined logistics, optimized inventory, and improved forecasting, manufacturers can increase operational efficiency, reduce costs, respond swiftly to any disruptions, and create more agile and resilient supply chains. As an example of the potential upside of using IoT to improve supply chain transparency, research from GEODIS indicated that 62% of companies have limited visibility of their supply chain and 15% only have visibility on production.
- Predictive Maintenance: IoT facilitates the transition from reactive to predictive maintenance by employing sensors, actuators, and tags to continuously monitor equipment. This real-time (or near real-time) data enables early identification of potential issues, allowing manufacturers to predict maintenance needs and optimize schedules. The result is reduced downtime, extended machinery lifespan, and lowered maintenance costs. SAP reports that by integrating IoT sensors and data analytics, manufacturers can reduce downtime by up to 50% and extend asset lifespan as much as 40%1.
- Production Quality Control and Defect Detection: IoT plays a pivotal role in elevating production quality control and defect detection. Through strategically placed sensors, actuators, and computer vision systems in the production environment, real-time data is continuously collected and analyzed to proactively identify defects and deviations from quality standards. V-Soft Consulting implemented smart manufacturing technologies, integrating computer vision and IoT, at Penn State’s manufacturing department. This initiative improved defect detection accuracy by 17%, reduced repair downtime by 10%, leading to cost savings of $150K per production line.2
IoT’s role as a key driver of Industry 4.0 lies in its ability to transform traditional manufacturing and industrial processes into intelligent, adaptive, and interconnected systems. Through this transformation, companies can improve operational efficiencies, reduce costs, and enhance supply chain resilience amid a rapidly evolving industrial landscape.
Case Study: Global Lighthouse Network (GLN)
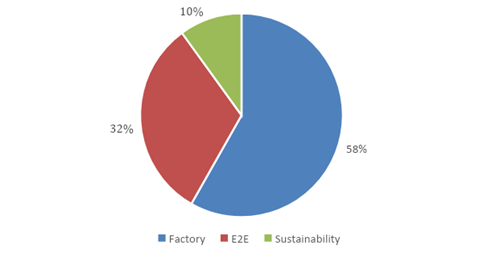
The World Economic Forum, in collaboration with McKinsey, launched the Global Lighthouse Network in 2018 to identify organizations and technologies at the forefront of Industry 4.0. The Lighthouses are categorized as:
- Factory: specific production site
- End-to-End (E2E): deploy technologies across their value chains
- Sustainability: demonstrate exemplary use of technology for emissions, waste, and water reduction
Each Lighthouse is recognized for its leadership in leveraging advanced technologies and strategies to drive growth, improve resilience, and deliver environmental sustainability.3 The Global Lighthouse Network has grown to 153 Lighthouses since its 2018 launch, split into the following categories:
Factory Lighthouse Example: Agilent Facility in Waldbronn, Germany4
Agilent Waldbronn unveiled over 25 Industry 4.0 roles and 20 corresponding use cases to tackle supply chain disruptions, changing product demands, and fluctuations in demand. Leveraging an Industry 4.0 toolkit, which included using Industrial IoT (IIoT) and AI for rapid simulation and prediction, the high-volume, high-mix life-science manufacturing site witnessed dramatic improvements. The facility achieved a 35% improvement in quality, a 44% increase in productivity, and a 48% rise in output, ultimately fueling market share growth.
The Global Lighthouse Network spotlights companies at the forefront of Industry 4.0. The Agilent facility in Germany serves as an illustration of deploying key technologies, including IoT, to drive dramatic improvements within a factory environment.
Conclusion
IoT acts as a unifying force across Industry 4.0 technologies by imbuing visibility and connectivity within factories and across supply chains. This interconnected ecosystem enhances efficiency, enables predictive capabilities, safeguards valuable assets, and fosters the next phase of smart manufacturing.
The future of Industry 4.0 is poised for continued transformation, marked by advancements in emerging technologies and evolving industrial practices. With the ongoing integration of IoT, AI, and data analytics, manufacturing processes will become increasingly intelligent, adaptive, and interconnected. Real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and data-driven decision-making will be pervasive, enhancing operational efficiency and responsiveness. Industry 4.0 also stands as a powerful catalyst for companies striving to achieve their sustainability goals by optimizing resources and reducing their environmental impacts.
About Positioning Universal
Established in 2013, Positioning Universal is a leading global provider of customizable IoT devices, GPS vehicle and asset monitoring solutions, and Systems Integration services. With a deep understanding of IoT technologies, Positioning Universal guides companies in designing and deploying the most suitable IoT solutions for their needs. By leveraging our expertise, companies can optimize the operation of fleets and assets used in Industry 4.0 programs. Our solutions and on-going support empower businesses with the invaluable business intelligence needed to maintain a competitive edge in rapidly evolving markets.
1 SAP, “What is Industry 4.0?” (www.sap.com/products/scm/industry-4-0/what-is-industry-4-0.html)
2 V-Soft Consulting, “Case Study: Computer Vision Detection,” (https://blog.vsoftconsulting.com/blog/case-study-computer-vision-defect-detection)
3 McKinsey, “What are Industry 4.0, the Fourth Industrial Revolution, and 4IR?” August 17, 2022 (https://www.mckinsey.com/featured-insights/mckinsey-explainers/what-are-industry-4-0-the-fourth-industrial-revolution-and-4ir)
4 World Economic Forum, “Factories of the Future Show How to Apply AI to Benefit People, Planet and Performance,” December 13, 2023 (https://www.weforum.org/press/2023/12/factories-of-the-future-show-how-to-apply-ai-to-benefit-people-planet-and-performance/)
Author
Geoff WeathersbyRelated posts
Exploring the Power of AI Algorithms in Telematics: Enhancing Efficiency and Safety
Introduction to AI Algorithms in Telematics Telematics has already transformed t
Positioning Universal: Leading the Way with GPS III Satellites and Unparalleled Accuracy
Embark on a new era of tracking precision and reliability with the upcoming mode
Harnessing AI-Powered Telematics for Improved Emergency Response
AI holds immense potential to further enhance the capabilities of telematics sol